
PHYSICAL LAYER RS-232 RS-449 ITU-T V-Series I.430 I.431 PDH SONET/SDH PON OTN DSL IEEE 802.3 IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802.15 IEEE 802.16 IEEE 1394 ITU-T G.hn PHY USB Bluetooth DATA LINK LAYER ATM ARP SDLC HDLC CSLIP SLIP GFP PLIP IEEE 802.2 LLC MAC L2TP IEEE 802.3 Frame Relay ITU-T G.hn DLL PPP X.25 LAPB Q.922 LAPF NETWORK LAYER IP IPv4 IPv6 ICMP IPsec IGMP IPX IS-IS AppleTalk X.25 PLP TRANSPORT LAYER TCP UDP SCTP DCCP SPX SESSION LAYER Named pipe NetBIOS SAP PPTP RTP SOCKS X.225[1] PRESENTATION LAYER MIME XDR ASN.1 ASCII PGP APPLICATION LAYER NNTP SIP SSI DNS FTP Gopher HTTP NFS NTP SMPP SMTP SNMP Telnet DHCP NETCONF
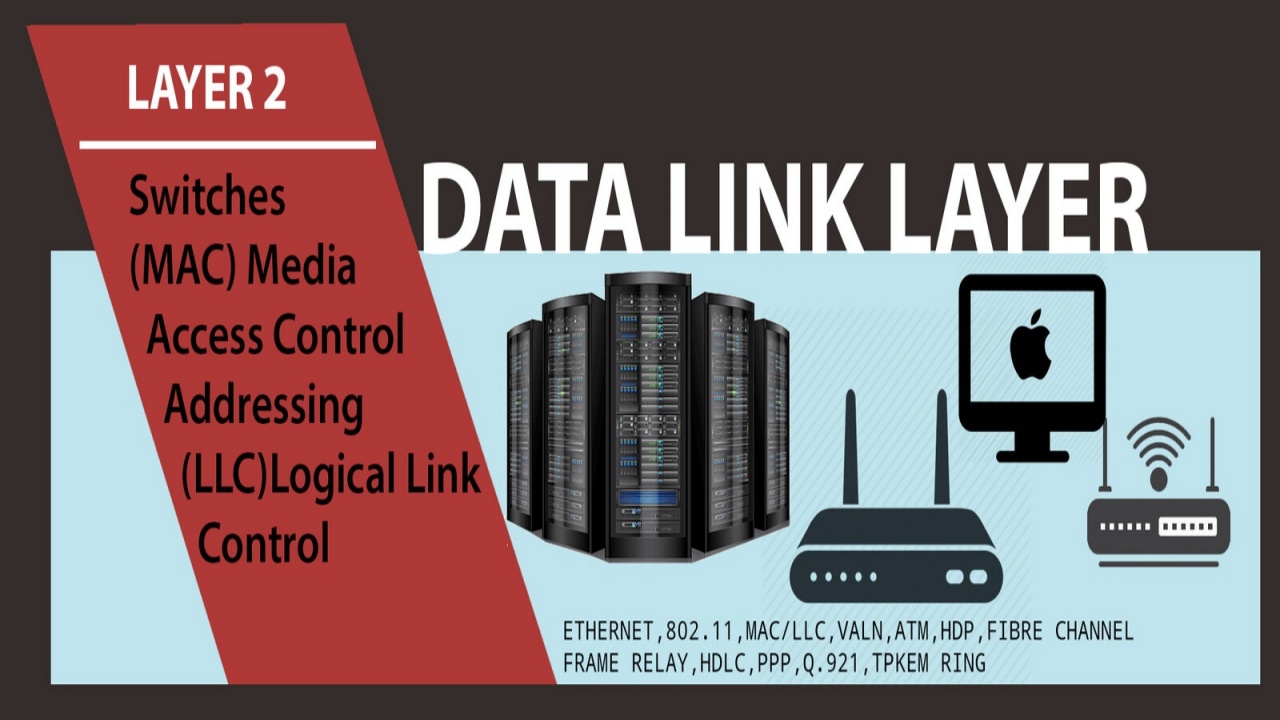
PHYSICAL LAYER RS-232 RS-449 ITU-T V-Series I.430 I.431 PDH SONET/SDH PON OTN DSL IEEE 802.3 IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802.15 IEEE 802.16 IEEE 1394 ITU-T G.hn PHY USB Bluetooth DATA LINK LAYER ATM ARP SDLC HDLC CSLIP SLIP GFP PLIP IEEE 802.2 LLC MAC L2TP IEEE 802.3 Frame Relay ITU-T G.hn DLL PPP X.25 LAPB Q.922 LAPF NETWORK LAYER IP IPv4 IPv6 ICMP IPsec IGMP IPX IS-IS AppleTalk X.25 PLP TRANSPORT LAYER TCP UDP SCTP DCCP SPX SESSION LAYER Named pipe NetBIOS SAP PPTP RTP SOCKS X.225[1] PRESENTATION LAYER MIME XDR ASN.1 ASCII PGP APPLICATION LAYER NNTP SIP SSI DNS FTP Gopher HTTP NFS NTP SMPP SMTP SNMP Telnet DHCP NETCONF
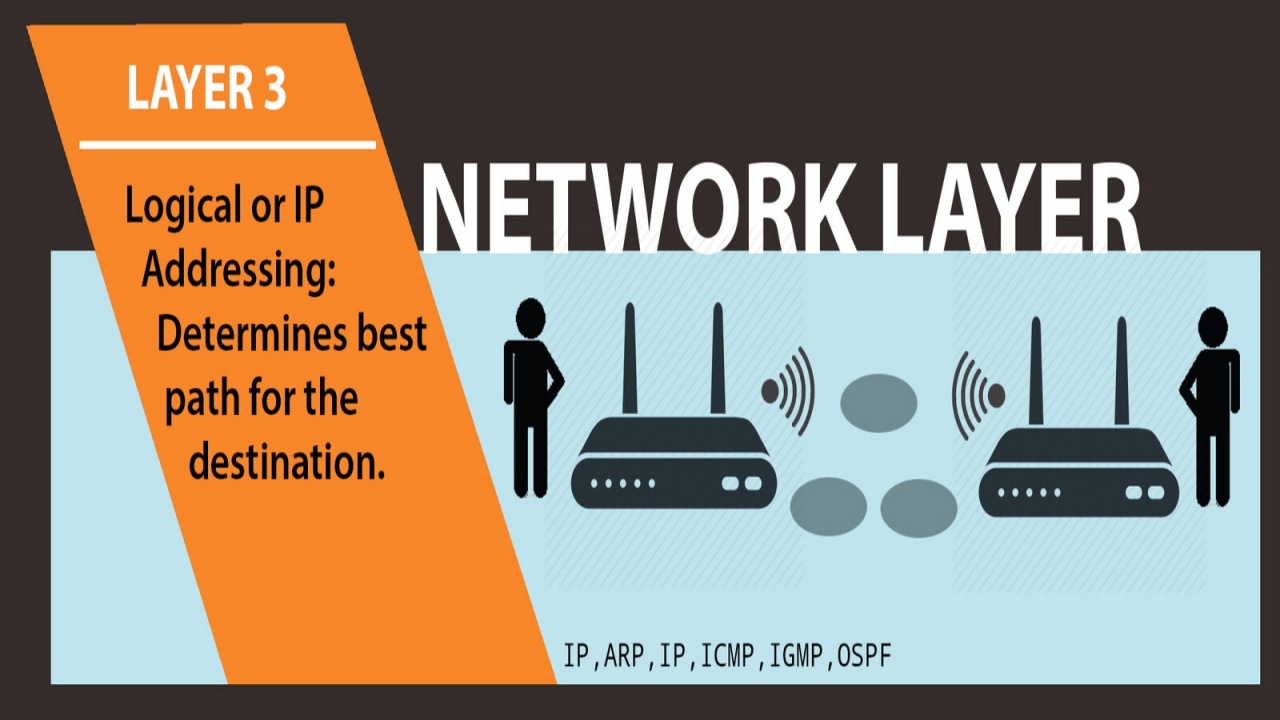
PHYSICAL LAYER RS-232 RS-449 ITU-T V-Series I.430 I.431 PDH SONET/SDH PON OTN DSL IEEE 802.3 IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802.15 IEEE 802.16 IEEE 1394 ITU-T G.hn PHY USB Bluetooth DATA LINK LAYER ATM ARP SDLC HDLC CSLIP SLIP GFP PLIP IEEE 802.2 LLC MAC L2TP IEEE 802.3 Frame Relay ITU-T G.hn DLL PPP X.25 LAPB Q.922 LAPF NETWORK LAYER IP IPv4 IPv6 ICMP IPsec IGMP IPX IS-IS AppleTalk X.25 PLP TRANSPORT LAYER TCP UDP SCTP DCCP SPX SESSION LAYER Named pipe NetBIOS SAP PPTP RTP SOCKS X.225[1] PRESENTATION LAYER MIME XDR ASN.1 ASCII PGP APPLICATION LAYER NNTP SIP SSI DNS FTP Gopher HTTP NFS NTP SMPP SMTP SNMP Telnet DHCP NETCONF
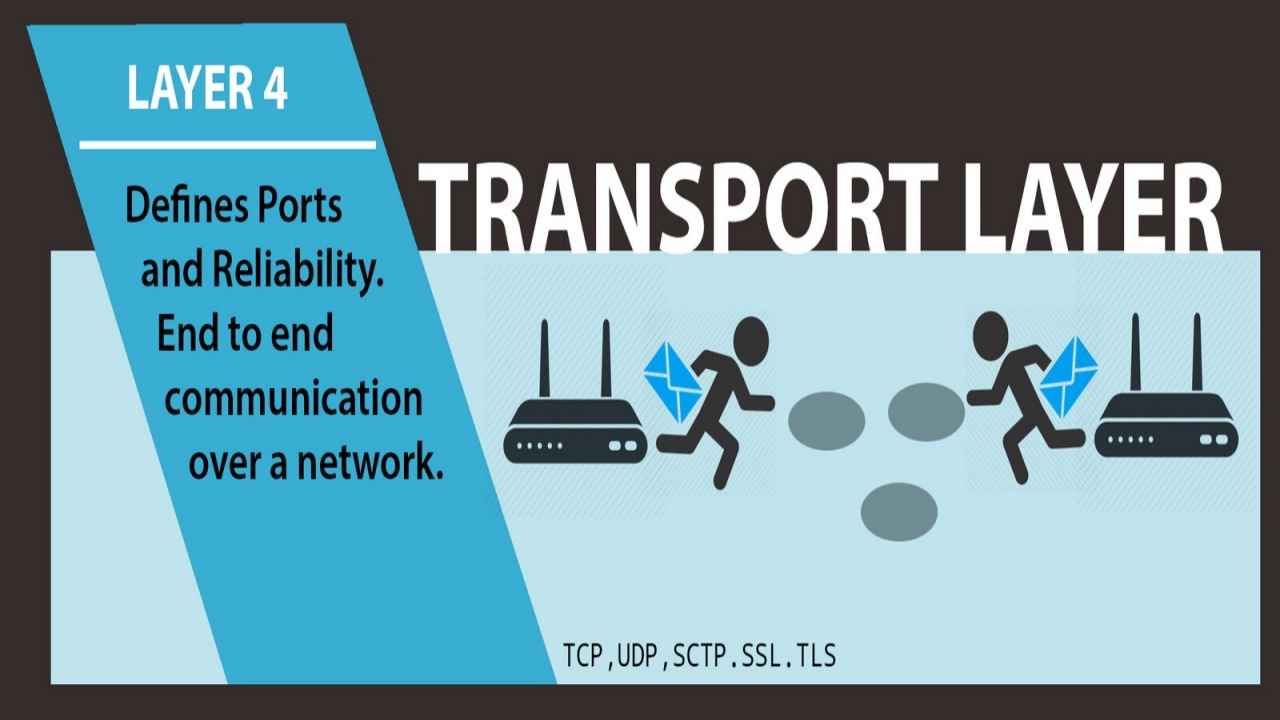
PHYSICAL LAYER RS-232 RS-449 ITU-T V-Series I.430 I.431 PDH SONET/SDH PON OTN DSL IEEE 802.3 IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802.15 IEEE 802.16 IEEE 1394 ITU-T G.hn PHY USB Bluetooth DATA LINK LAYER ATM ARP SDLC HDLC CSLIP SLIP GFP PLIP IEEE 802.2 LLC MAC L2TP IEEE 802.3 Frame Relay ITU-T G.hn DLL PPP X.25 LAPB Q.922 LAPF NETWORK LAYER IP IPv4 IPv6 ICMP IPsec IGMP IPX IS-IS AppleTalk X.25 PLP TRANSPORT LAYER TCP UDP SCTP DCCP SPX SESSION LAYER Named pipe NetBIOS SAP PPTP RTP SOCKS X.225[1] PRESENTATION LAYER MIME XDR ASN.1 ASCII PGP APPLICATION LAYER NNTP SIP SSI DNS FTP Gopher HTTP NFS NTP SMPP SMTP SNMP Telnet DHCP NETCONF
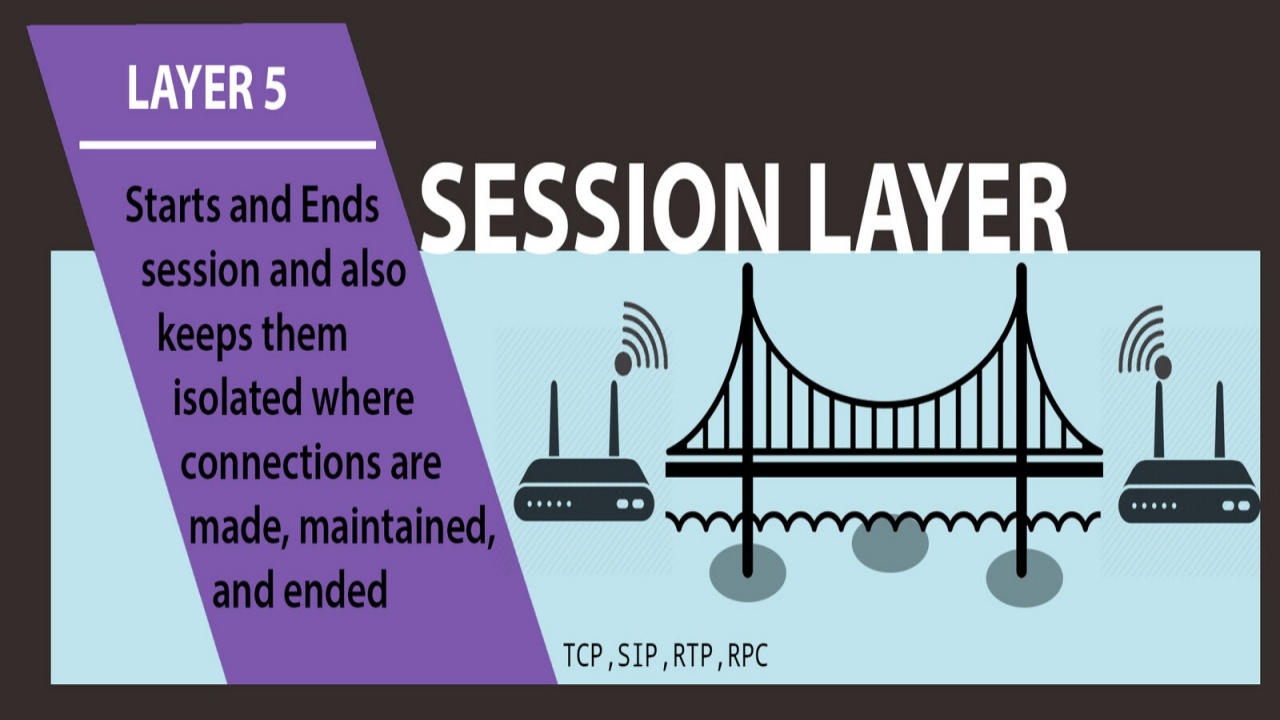
PHYSICAL LAYER RS-232 RS-449 ITU-T V-Series I.430 I.431 PDH SONET/SDH PON OTN DSL IEEE 802.3 IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802.15 IEEE 802.16 IEEE 1394 ITU-T G.hn PHY USB Bluetooth DATA LINK LAYER ATM ARP SDLC HDLC CSLIP SLIP GFP PLIP IEEE 802.2 LLC MAC L2TP IEEE 802.3 Frame Relay ITU-T G.hn DLL PPP X.25 LAPB Q.922 LAPF NETWORK LAYER IP IPv4 IPv6 ICMP IPsec IGMP IPX IS-IS AppleTalk X.25 PLP TRANSPORT LAYER TCP UDP SCTP DCCP SPX SESSION LAYER Named pipe NetBIOS SAP PPTP RTP SOCKS X.225[1] PRESENTATION LAYER MIME XDR ASN.1 ASCII PGP APPLICATION LAYER NNTP SIP SSI DNS FTP Gopher HTTP NFS NTP SMPP SMTP SNMP Telnet DHCP NETCONF
PHYSICAL LAYER RS-232 RS-449 ITU-T V-Series I.430 I.431 PDH SONET/SDH PON OTN DSL IEEE 802.3 IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802.15 IEEE 802.16 IEEE 1394 ITU-T G.hn PHY USB Bluetooth DATA LINK LAYER ATM ARP SDLC HDLC CSLIP SLIP GFP PLIP IEEE 802.2 LLC MAC L2TP IEEE 802.3 Frame Relay ITU-T G.hn DLL PPP X.25 LAPB Q.922 LAPF NETWORK LAYER IP IPv4 IPv6 ICMP IPsec IGMP IPX IS-IS AppleTalk X.25 PLP TRANSPORT LAYER TCP UDP SCTP DCCP SPX SESSION LAYER Named pipe NetBIOS SAP PPTP RTP SOCKS X.225[1] PRESENTATION LAYER MIME XDR ASN.1 ASCII PGP APPLICATION LAYER NNTP SIP SSI DNS FTP Gopher HTTP NFS NTP SMPP SMTP SNMP Telnet DHCP NETCONF

PHYSICAL LAYER RS-232 RS-449 ITU-T V-Series I.430 I.431 PDH SONET/SDH PON OTN DSL IEEE 802.3 IEEE 802.11 IEEE 802.15 IEEE 802.16 IEEE 1394 ITU-T G.hn PHY USB Bluetooth DATA LINK LAYER ATM ARP SDLC HDLC CSLIP SLIP GFP PLIP IEEE 802.2 LLC MAC L2TP IEEE 802.3 Frame Relay ITU-T G.hn DLL PPP X.25 LAPB Q.922 LAPF NETWORK LAYER IP IPv4 IPv6 ICMP IPsec IGMP IPX IS-IS AppleTalk X.25 PLP TRANSPORT LAYER TCP UDP SCTP DCCP SPX SESSION LAYER Named pipe NetBIOS SAP PPTP RTP SOCKS X.225[1] PRESENTATION LAYER MIME XDR ASN.1 ASCII PGP APPLICATION LAYER NNTP SIP SSI DNS FTP Gopher HTTP NFS NTP SMPP SMTP SNMP Telnet DHCP NETCONF
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model is a conceptual model created by the International Organization for Standardization which enables diverse communication systems to communicate using standard protocols. The OSI Model provides a standard for different computer systems to be able to communicate with each other.
The OSI Model can be seen as a universal language for computer networking. It is based on the concept of splitting up a communication system into seven abstract layers, each one stacked upon the last.

