Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) assigns IP addresses to network endpoints so they can communicate with other network endpoints over IP.
Domain Name Service (DNS) database translates the domain names into IP addresses.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) allows users to transfer files from one machine to another.
HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) designed for transferring a hypertext among two or more systems. HTML tags are used for creating links.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) used for transferring data between the client browser (request) and the web server (response)
in the hypertext format, same in case of HTTPS except that the transferring of data is done in an encrypted format.
Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) to receive email messages by connecting to the email server to view and edit messages without downloading them.
Internet Protocol (IP) addresses in packets help in routing them through different nodes in a network until it reaches the destination system.
Post Office Protocol (POP) designed for receiving incoming emails.
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) communicates between two routers directly without any host or any other networking in between to provide loop
detection authentication, transmission encryption and data compression.
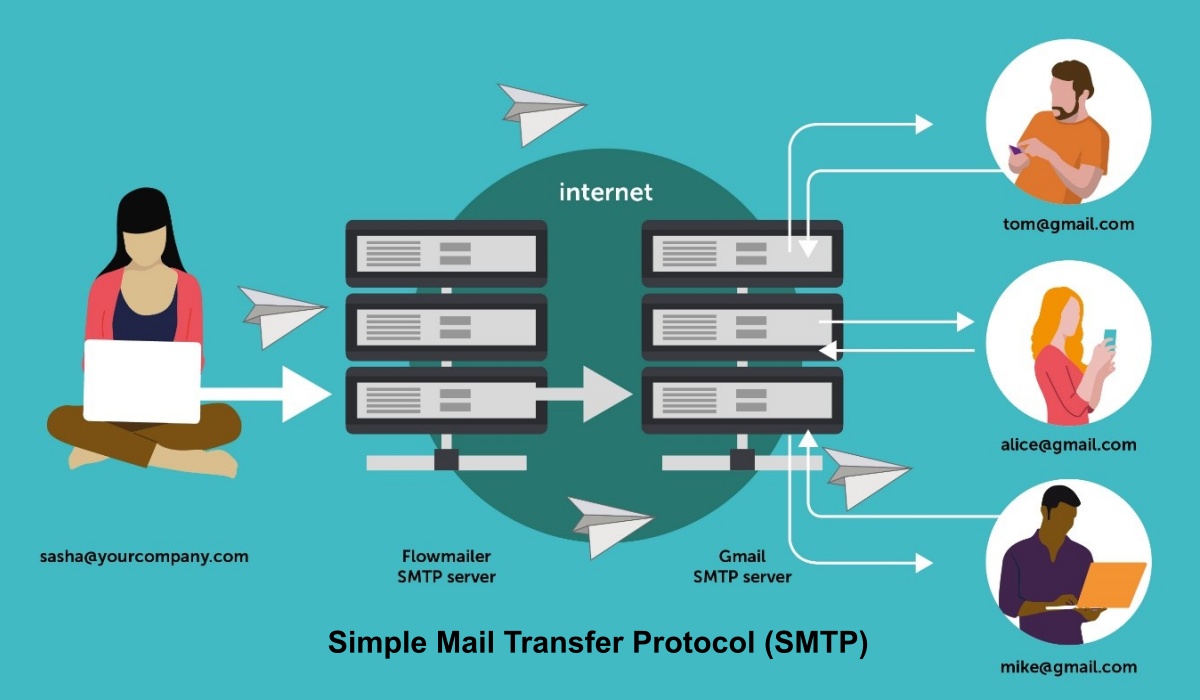
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) designed to send and distribute outgoing email.
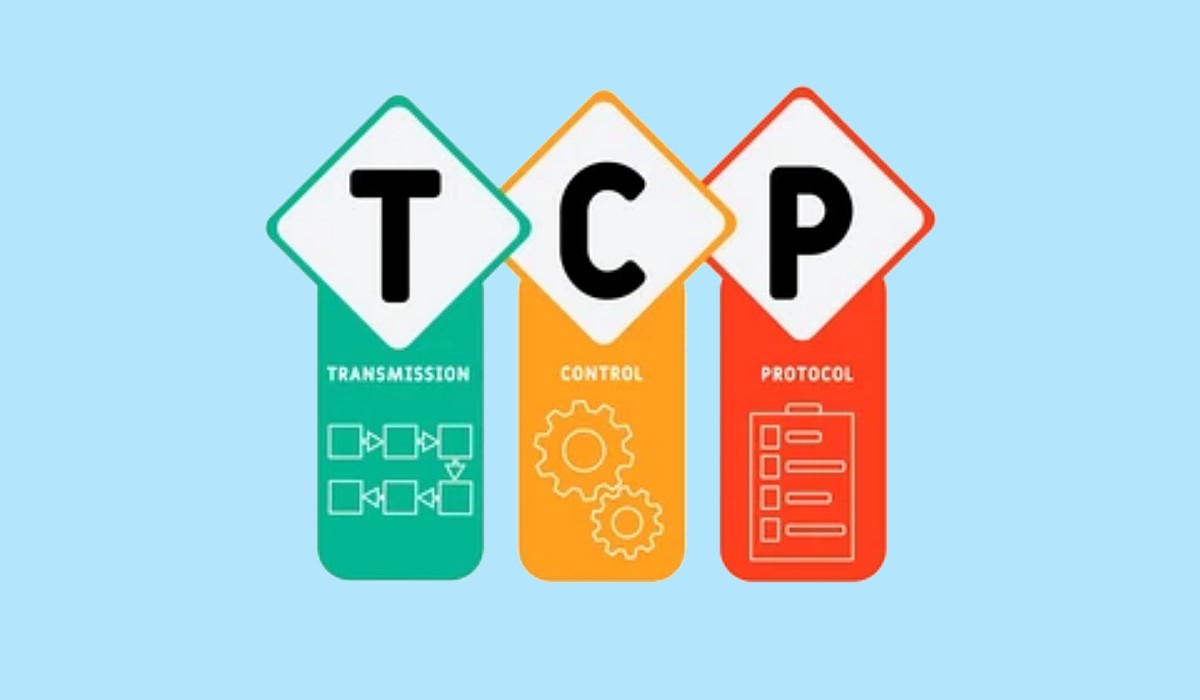
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) used for communicating over a network that divides messages into series of packets that are sent from source
to destination and there it gets reassembled at the destination.
Terminal Network (TELNET) designed for remote connectivity, and it establishes connections between a remote endpoint and a host machine to enable
a remote session.